INDICATION
REXULTI is indicated for use as an adjunctive therapy to antidepressants for the treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD) in adults.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
WARNING: INCREASED MORTALITY IN ELDERLY PATIENTS WITH DEMENTIA-RELATED PSYCHOSIS
Elderly patients with dementia-related psychosis treated with antipsychotic drugs are at increased risk of death. REXULTI is not approved for the treatment of patients with dementia-related psychosis without agitation associated with dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease.
WARNING: SUICIDAL THOUGHTS AND BEHAVIORS
Antidepressants increased the risk of suicidal thoughts and behaviors in patients aged 24 years and younger. Monitor for clinical worsening and emergence of suicidal thoughts and behaviors. The safety and effectiveness of REXULTI have not been established in pediatric patients with MDD.
Please continue watching for additional Important Safety Information including the BOXED WARNING and please see Full Prescribing Information at www.REXULTIhcp.com.
For your awareness, the activity of these compounds is based on in vitro data. The clinical significance of the in vitro data is unknown. The mechanism of action of REXULTI is unknown.
My name is Dr. Rakesh Jain and today we're going to discuss how REXULTI is thought to work.
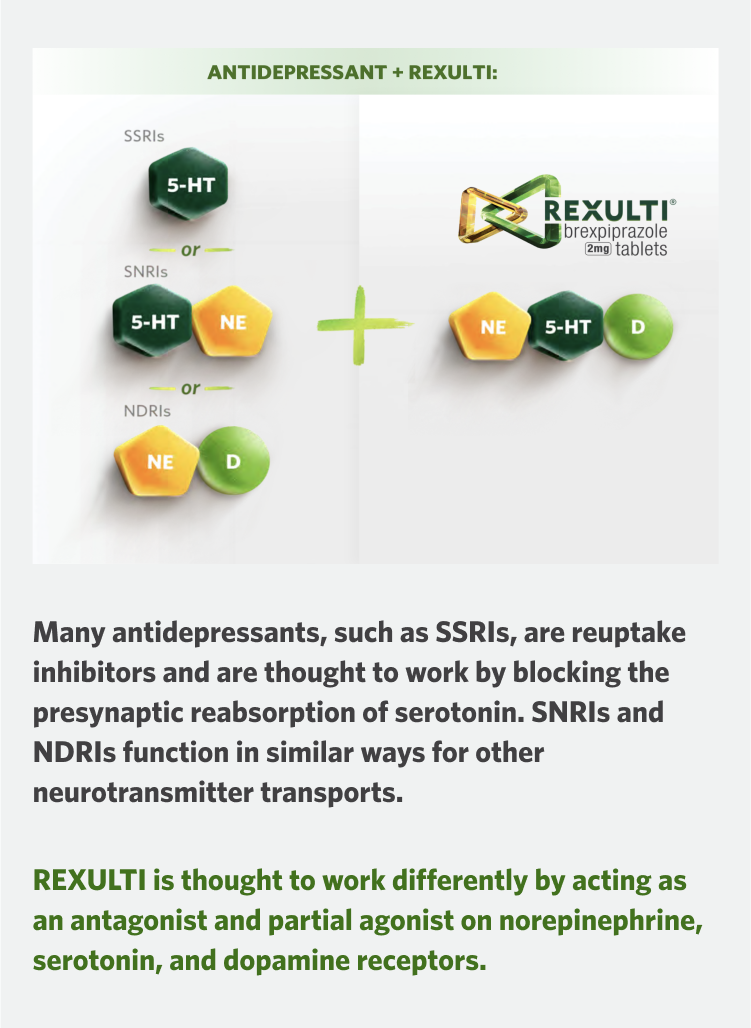
REXULTI and antidepressants both interact with some of the same neurotransmitter systems implicated in depression, but in different ways.
Some antidepressants, such as SSRIs, SNRIs, and NDRIs, are reuptake inhibitors that are thought to work on one or two types of neurotransmitter receptors.
SSRIs inhibit the reuptake of serotonin, SNRIs inhibit the reuptake of both serotonin and norepinephrine, while NDRIs inhibit the reuptake of norepinephrine and dopamine.
Reuptake inhibitors, such as SSRIs, work by blocking the presynaptic reabsorption of serotonin. SNRIs and NDRIs function in similar ways for other neurotransmitter transporters.
REXULTI is thought to work differently than reuptake inhibitors, as a partial agonist and antagonist.
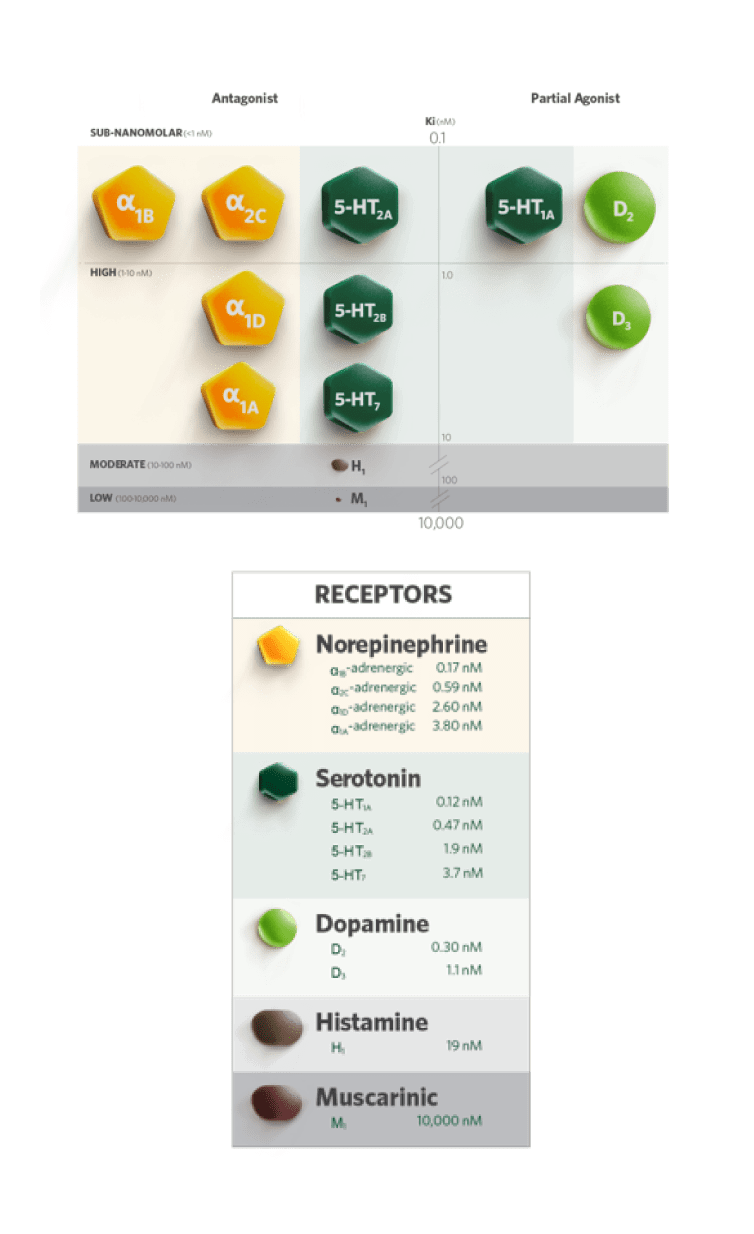
REXULTI has high binding affinity to three types of neurotransmitter receptors—norepinephrine, serotonin, and dopamine.
REXULTI binds directly to the receptor, and acts as a partial agonist across some dopamine and serotonin receptors and as an antagonist across some norepinephrine and serotonin receptors.
REXULTI acts as an antagonist at norepinephrine α1B, α2C, α1D, and α1A receptors.
REXULTI acts as a partial agonist at serotonin 5-HT1A receptors, but also as an antagonist at serotonin 5-HT2A, 5-HT2B, and 5-HT7 receptors.
REXULTI acts as a partial agonist at both dopamine D2 and D3 receptors.
These neurotransmitters exert their effects not only individually, but also by modulating each other's activity.
REXULTI and antidepressants may work together, but in different ways, on some of the same neurotransmitter receptors implicated in depression. Most antidepressants work through reuptake inhibition while REXULTI is both a direct partial agonist and antagonist of these systems. Please continue listening for additional Important Safety Information.
INDICATION and IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION for REXULTI (brexpiprazole)
INDICATION
REXULTI is indicated for use as an adjunctive therapy to antidepressants for the treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD) in adults.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
WARNING: INCREASED MORTALITY IN ELDERLY PATIENTS WITH DEMENTIA-RELATED PSYCHOSIS
Elderly patients with dementia-related psychosis treated with antipsychotic drugs are at increased risk of death. REXULTI is not approved for the treatment of patients with dementia-related psychosis without agitation associated with dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease.
WARNING: SUICIDAL THOUGHTS AND BEHAVIORS
Antidepressants increased the risk of suicidal thoughts and behaviors in patients aged 24 years and younger. Monitor for clinical worsening and emergence of suicidal thoughts and behaviors. The safety and effectiveness of REXULTI have not been established in pediatric patients with MDD.
Contraindication: In patients with known hypersensitivity to brexpiprazole or any of its components. Reactions have included: rash, facial swelling, urticaria and anaphylaxis.
Cerebrovascular Adverse Events, Including Stroke: In clinical trials, elderly patients with dementia randomized to risperidone, aripiprazole, and olanzapine had a higher incidence of stroke and transient ischemic attack, including fatal stroke. REXULTI is not approved for the treatment of patients with dementia-related psychosis without agitation associated with dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease.
Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS): NMS is a potentially fatal symptom complex reported in association with administration of antipsychotic drugs, including REXULTI. Clinical signs of NMS are hyperpyrexia, muscle rigidity, altered mental status, and evidence of autonomic instability (irregular pulse or blood pressure, tachycardia, diaphoresis and cardiac dysrhythmia). Additional signs may include elevated creatinine phosphokinase, myoglobinuria (rhabdomyolysis), and acute renal failure. Manage NMS with immediate discontinuation of REXULTI, intensive symptomatic treatment, and monitoring.
Tardive Dyskinesia (TD): Risk of TD, and the potential to become irreversible, appear to increase with duration of treatment and total cumulative dose of antipsychotic drugs. TD can develop after relatively brief treatment periods, at low doses, or after discontinuation of treatment. For chronic treatment, use the lowest dose and shortest duration of REXULTI needed to produce a clinical response. If signs and symptoms of TD appear, drug discontinuation should be considered.
Metabolic Changes: Atypical antipsychotic drugs, including REXULTI, have caused metabolic changes including:
- Hyperglycemia/Diabetes Mellitus: Hyperglycemia and diabetes mellitus, in some cases extreme and associated with diabetic ketoacidosis, hyperosmolar coma or death, have been reported in patients treated with atypical antipsychotics. Assess fasting plasma glucose before or soon after initiation of antipsychotic medication and monitor periodically during long-term treatment.
- Dyslipidemia: Atypical antipsychotics cause adverse alterations in lipids. Before or soon after initiation of antipsychotic medication, obtain a fasting lipid profile at baseline and monitor periodically during treatment.
- Weight Gain: Weight gain has been observed in patients treated with REXULTI. Monitor weight at baseline and frequently thereafter.
Pathological Gambling and Other Compulsive Behaviors: Intense urges, particularly for gambling, and the inability to control these urges have been reported while taking REXULTI. Other compulsive urges have been reported less frequently. Prescribers should ask patients or their caregivers about the development of new or intense compulsive urges. Consider dose reduction or stopping REXULTI if such urges develop.
Leukopenia, Neutropenia, and Agranulocytosis: Leukopenia and neutropenia have been reported with antipsychotics. Agranulocytosis (including fatal cases) has been reported with other agents in this class. Monitor complete blood count in patients with pre-existing low white blood cell count (WBC)/absolute neutrophil count or history of drug-induced leukopenia/neutropenia. Discontinue REXULTI at the first sign of a clinically significant decline in WBC and in patients with severe neutropenia.
Orthostatic Hypotension and Syncope: Atypical antipsychotics cause orthostatic hypotension and syncope. Generally, the risk is greatest during initial dose titration and when increasing the dose. Monitor in patients vulnerable to hypotension, and those with cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases.
Falls: Antipsychotics may cause somnolence, postural hypotension, motor, and sensory instability, which may lead to falls causing fractures or other injuries. For patients with diseases, conditions, or medications that could exacerbate these effects, complete fall risk assessments when initiating treatment and recurrently during therapy.
Seizures: REXULTI may cause seizures and should be used with caution in patients with a history of seizures or with conditions that lower the seizure threshold.
Body Temperature Dysregulation: Use REXULTI with caution in patients who may experience conditions that increase body temperature (e.g., strenuous exercise, extreme heat, dehydration, or concomitant use with anticholinergics).
Dysphagia: Esophageal dysmotility and aspiration have been associated with antipsychotics, including REXULTI, and should be used with caution in patients at risk for aspiration.
Potential for Cognitive and Motor Impairment: REXULTI has the potential to impair judgment, thinking, or motor skills. Patients should be cautioned about operating hazardous machinery, including operating motor vehicles, until they are reasonably certain REXULTI does not affect them adversely.
Concomitant Medication: Dosage adjustments are recommended in patients who are known cytochrome P450 (CYP) 2D6 poor metabolizers and in patients taking concomitant CYP3A4 inhibitors or CYP2D6 inhibitors or strong CYP3A4 inducers.
Most commonly observed adverse reactions: In clinical trials of adults, the most common adverse reactions were:
- Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) (adjunctive treatment to antidepressant therapy; ≥5% incidence and at least twice the rate of placebo for REXULTI vs. placebo): weight increased, somnolence, and akathisia.
Dystonia: Symptoms of dystonia may occur in susceptible individuals during the first days of treatment and at low doses.
Pregnancy: Adequate and well-controlled studies to assess the risks of REXULTI during pregnancy have not been conducted. REXULTI should be used during pregnancy only if the benefit justifies the risk to the fetus.
Lactation: It is not known if REXULTI is excreted in human breast milk. A decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Otsuka America Pharmaceutical, Inc. at 1-800-438-9927 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 (www.fda.gov/medwatch).
Please see FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION, including BOXED WARNING, at REXULTIhcp.com.
To learn more about REXULTI, visit REXULTIhcp.com/MDD.